New ferry route to connect capital Dili to Oecusse enclave and Ataúro.
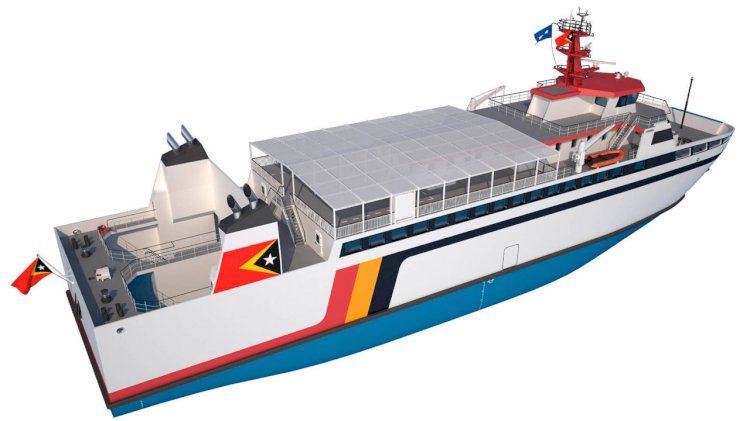
Recently, the Republic of Timor-Leste and Damen Shipyards Group signed a contract agreeing provision of a new RoPax Ferry 6716. The vessel will operate a route between the Timor-Leste capital Dili, the Oecusse enclave and the island of Ataúro, providing regular transportation of passengers, vehicles and goods on the north coast of the island.
The contract was signed at the Kay Rala Xanana Gusmão Hall of the Ministry of Finance, Díli, by the Minister of Transport and Communications, José Agustinho da Silva, and by the regional director of Damen Shipyards, Gysbert Boersma.
With an ageing vessel currently in operation, the Port Authority of Timor-Leste IP (APORTIL) recognises the need to maintain the safety and reliability of its fleet, hence the investment in a new ship. In a project co-financed by Timor-Leste and the Government of Germany, the RoPax Ferry 6716 is scheduled to begin operations in 2021, and will lower operation costs, increase reliability of the service, and improve employment opportunities due to the improvement in transportation networks. In preparation for the ferry’s arrival, over the next 19 months APORTIL will undertake work to improve and build support infrastructures.
The extension of these maritime passenger connections will initially include a connection between Dili and Com, in addition to those already in place between Díli, Ataúro and Oecusse, with the aim of improving the quality of life of the populations in these areas.
In a speech delivered at the contract signing, Timor-Leste Minister of Transport and Communications José Agustinho da Silva said:
“This new ferry will help to connect Dili with other ports on the south and east coasts of Timor-Leste and improve access to market, education and institutions in Dili and provide other important services to Timor-Leste.”
The Minister went on to say:
“This new ferry will increase job opportunities to our seafarers and give direct and long-term employment opportunities to our Timorese seafarers.”
The RoPax Ferry 6716 will have a width of 16 metres, a draft of 3.3 metres and a length of 67.3 metres, and its deck, with a 27-ton axle load, will reach 4.8 metres in height. The vessel is capable of a maximum speed of 10 knots and will have a carrying capacity of 380 pax.
Damen’s design and proposal engineer on the project, Gökçe Koc, explains why the vessel is ideal for Timor-Leste:
“The vessel’s two Yanmar engines, delivering 837 kilowatts of power to a 1.6 metre fixed pitch propeller, give it the power to manoeuvre safely when docking as well as on the open water. It’s a remarkably stable vessel and combines high levels of comfort for the passengers along with high performance for the operator. APORTIL couldn’t have made a better choice.”
Damen will conduct the design and management of the project at its head office in the Netherlands and construction of the vessel will take place at Damen’s Yichang Shipyard in China. Upon completion of its construction, the vessel will be delivered to Dili.
Gysbert addressed the assembled representatives, saying:
“I hope this project will be the start of a long-lasting cooperation between the Republic of Timor-Leste and the Damen Shipyards Group. It is a privilege to contribute to the improved mobility of the Timor East people. With this ferry, in 19 months, Timor-Leste will receive a high quality vessel that will last for a generation.”