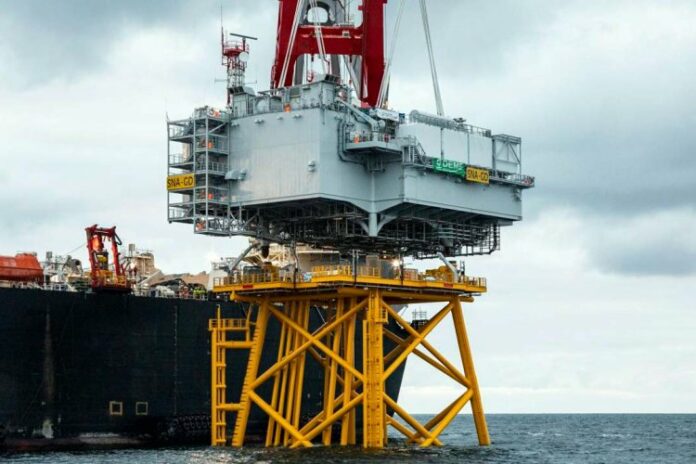
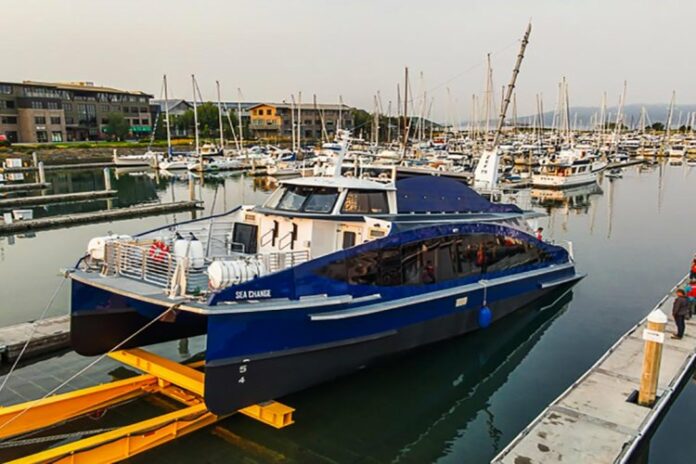
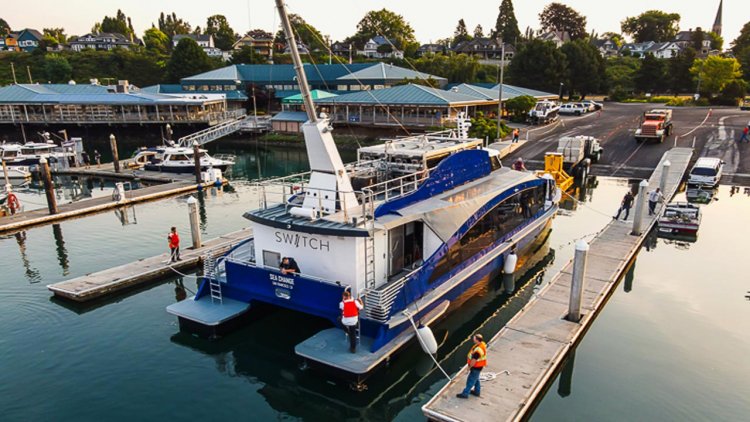
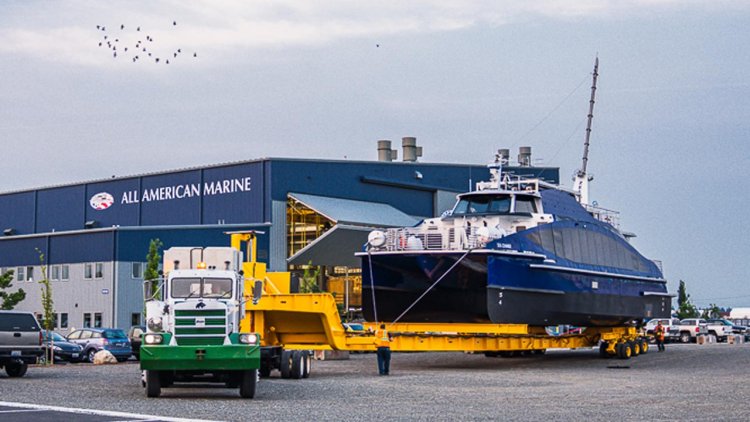
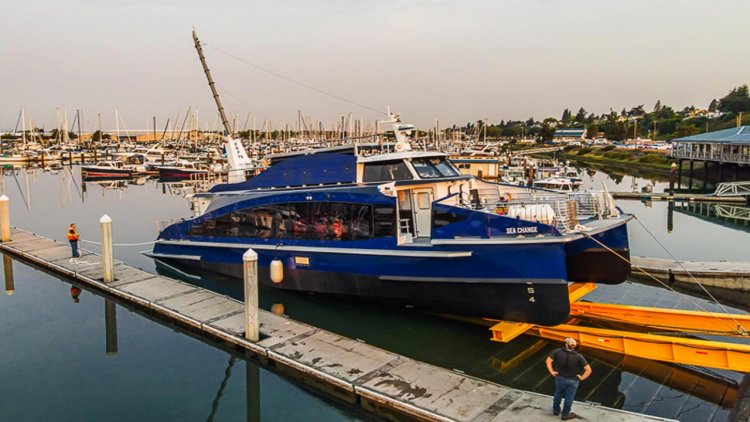
Weighing 2,100 tons, the OSS was successfully installed at the Saint-Nazaire offshore wind farm on August 18.
The electrical substation was constructed by a consortium including Atlantique Offshore Energy, the business unit of Chantiers de l’Atlantique dedicated to Renewable Marine Energies, GE Grid Solutions and DEME Group’s French subsidiary SDI. The 480 MW Saint-Nazaire offshore wind project is being developed by EDF Renouvelables and EIH S.à r.l, an indirect subsidiary of Enbridge Inc., and CPP Investments. Saint-Nazaire, scheduled to be operational in 2022, is the first commercial offshore wind farm installed in French waters. The contract for the substation was awarded in 2019.
Installed with the ‘Pioneering Spirit’, the 480 MW substation is (H) 15 m x 27 m x 39 m, while the jacket is 26 m x 26 m x 48 m (H) and weighs 1,250 tons.
The ACS division of GE Grid Solutions, located in Saint-Priest, France, designed and integrated the high and medium voltage systems. Those include five 220 kV gas insulated switchgears from Aix Les Bains, France, two 220/33kV transformers manufactured in Monchengladbach, Germany, two SCADA systems developed in Montpellier, France and one 33kV gas insulated switchgears and a telecommunication syste
DEME Offshore carried out the transport and installation of the OSS, including the offshore pre-piling works. Chantiers de l’Atlantique is responsible for the topside and jacket foundation design, manufacturing and commissioning. GE Grid Solutions is responsible for the high voltage electrical equipment and protection control systems design, manufacturing and commissioning.
Bart De Poorter, General Manager DEME Offshore Renewables, commented:
“The construction and installation of the OSS is the result of strong cooperation between the consortium members, with each partner bringing its expertise and highest level of execution to the project, enabling us to meet the stringent quality, safety and environmental standards. As a result of this cooperation, we were able to design, fabricate and install the OSS in only 26 months, which is an incredible achievement and testament to the collaboration with our partners. At DEME, we are certainly very proud that our expertise has played such a significant role in reaching this key milestone in the renewables industry, with Saint-Nazaire due to be the first commercial offshore wind farm in France.”
Frédéric Grizaud, Director of the BU Atlantique Offshore Energy at Chantiers de l’Atlantique, added:
“With the installation as scheduled of a new electrical substation designed and built by Atlantique Offshore Energy, we demonstrated once again our expertise, along with our partners, to manage a complex project to the satisfaction of our customer. We look forward to reaching the same level of performance for the future projects managed by the consortium”.
The same consortium responsible for Saint-Nazaire has also been selected by Eoliennes Offshore des Hautes Falaises et Eoliennes Offshore du Calvados to design, manufacture and install the electrical substations for the Fécamp and Calvados (Courseulles-sur-Mer) wind farms in Normandy, France.