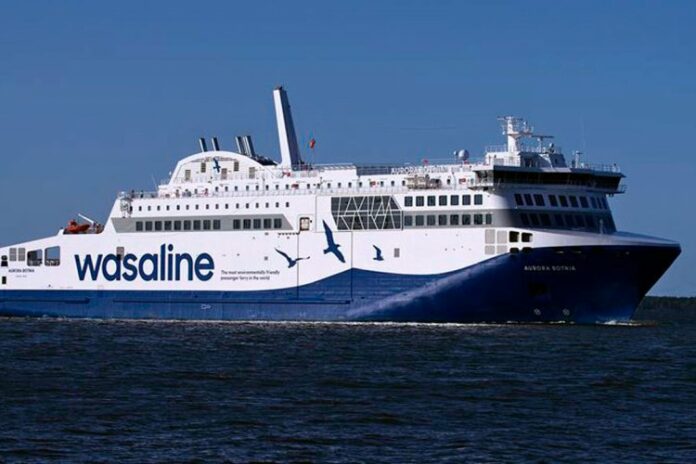
The technology group Wärtsilä and Wasaline, the Finnish–Swedish ferry operator, have signed a ten-year Optimised Maintenance agreement covering the company’s new ferry, the ‘Aurora Botnia’.
The agreement was signed in June 2021, but became effective in September. Built at the RMC shipyard in Finland, the Aurora Botnia is the most environmentally-friendly RoPax ferry in the world. The ship’s propulsion is based on a hybrid solution featuring the highly efficient Wärtsilä 31DF dual-fuel engine and batteries. The Wärtsilä 31DF will operate primarily on LNG fuel but will also be able to use BioLNG, a totally renewable fuel that can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 90 percent compared to conventional marine fuels. It emits no particulate matter (PM), and close to zero levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx).
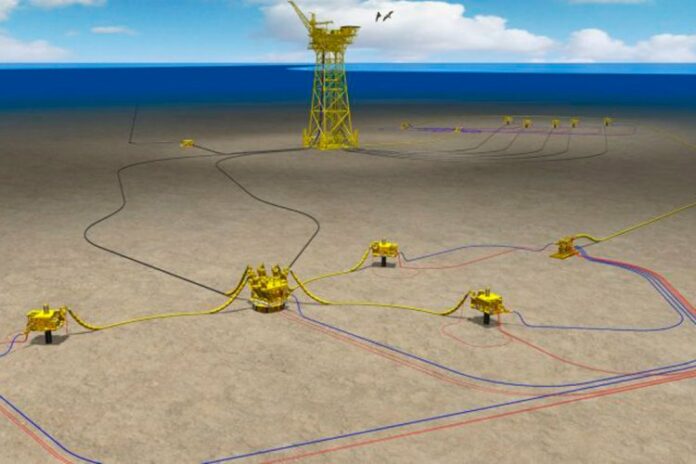
The comprehensive Wärtsilä Optimised maintenance agreement includes the latest digital solutions based on artificial intelligence to provide effective predictive maintenance support and the ability to identify potential faults before they actually happen. The service also makes it possible to tune the operation to achieve the lowest possible carbon footprint and minimise unscheduled downtime. The vessel will act as a floating test laboratory linked to Wärtsilä’s Smart Technology Hub in Vaasa, Finland, allowing real-time operational monitoring. This will maximise efficiency and provide valuable data for future developments of solutions capable of the highest levels of sustainability.
Peter Ståhlberg, Managing Director, Wasaline, says:
“We have worked closely with Wärtsilä for a long time and this partnership has paid huge dividends in terms of efficiency and environmental sustainability. We had no hesitation, therefore, in opting for a Wärtsilä maintenance agreement for this new ship, which will be the first car and passenger ferry in the world to have a Clean Design class notation. It already now meets the proposed ‘EU fit for 55’ programme, which seeks a reduction in CO2 emissions of 55 % by 2030.”
In addition to the hybrid propulsion system, the Aurora Botnia also features Wärtsilä’s Data Bridge platform. This enables advanced data analytics that provide insight into the ship’s performance at all times, thereby unlocking further potential for enhancing operational and technical efficiencies.
The ship will operate with four Wärtsilä 31DF engines, Wärtsilä’s LNG Pac gas storage solution, as well as with Wärtsilä thrusters, catalysators, controls, integrated electrical and automation systems, and an energy and power management system controlling the hybrid power solution. The ferry also features Wärtsilä’s Nacos Platinum integrated vessel control system.
The 150 metre long ferry will have an 800 passenger capacity and 1500 lane metres for vehicles. It will sail between Vaasa in Finland and Umeå in Sweden. Both ports will provide LNG bunkering facilities and battery charging capability. The eco-friendly vessel will help preserve the Kvarken World Heritage site through which it will operate.