The application by the Zero Carbon Humber (ZCH) Partnership is a first step to creating the world’s first net zero industrial cluster by 2040 and will support clean growth in the north-east of England. The bid, announced today, for Phase Two funding from the UK Government’s Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, builds on a successful application for Phase One funding which was announced in April.
The ZCH Partnership includes Equinor, Associated British Ports, British Steel, Centrica Storage Ltd, Drax Group, Mitsubishi, National Grid Ventures, px Group, SSE Thermal, Saltend Cogeneration Company Limited, Uniper, and the University of Sheffield’s Advanced Manufacturing Centre (AMRC).
Al Cook, Equinor executive vice president and UK country manager, says:
“We are proud to be a leader of Zero Carbon Humber, partnering with a broad group of forward-looking companies. This proposal can bring tremendous benefits to the Humber region, protecting industries, creating jobs, promoting economic growth and reducing emissions. Our bid demonstrates the kind of ambitious action that is needed to for the UK to achieve its net zero carbon target by 2050.”
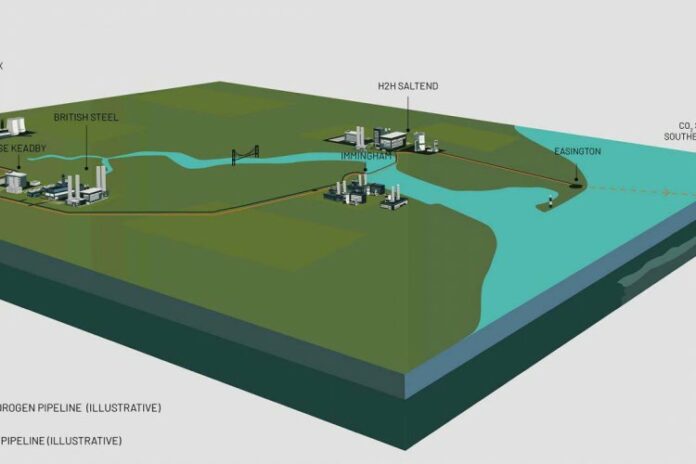
The bid centres around two elements, the first being the Equinor-led H2H Saltend (Hydrogen to Humber Saltend) hydrogen project at Saltend Chemicals Park near the city of Hull. H2H Saltend will be largest plant of its kind in the world to convert natural gas to hydrogen, combining a 600 megawatt autothermal reformer with carbon capture. From first production H2H Saltend will reduce industrial emissions by nearly 900,000 tonnes per year.
The second element is the hydrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2) pipeline network developed by National Grid Ventures that aims to link H2H Saltend to other industrial sites in the Humber region, enabling them in turn to fuel switch to hydrogen or capture their emissions. These sites include Drax Power station, SSE Thermal’s Keadby site, Uniper’s Killingholme site and British Steel at Scunthorpe.
Grete Tveit, Equinor senior vice president for low carbon solutions, says:
“We believe in the necessity of hydrogen and carbon capture to clean up heavy industry which is required to reach net zero targets. The technologies are proven and it’s now a question of putting them together. We and our partners have made great progress in our plans to decarbonise the Humber, through working with and learning from each other and also in engaging with national and local stakeholders. We are convinced that by continuing to work together we can make this happen.”
CO2 emissions from H2H Saltend and the other Humber sites will be transported by pipeline to Easington on the Yorkshire coast and then offshore to permanent storage under the Southern North Sea on the UK continental shelf. A consortium of world-class energy companies including Equinor is working to develop the offshore transport and storage infrastructure, and this network will be shared with the Teesside industrial cluster, where Equinor is also a partner in the Net Zero Teesside decarbonisation project.
The total size of the ZCH proposal is GBP 75 million, comprising private and public funding. The funds will be used to progress work towards a final investment decision during 2023 with H2H Saltend and the associated infrastructure potentially coming online in 2026.