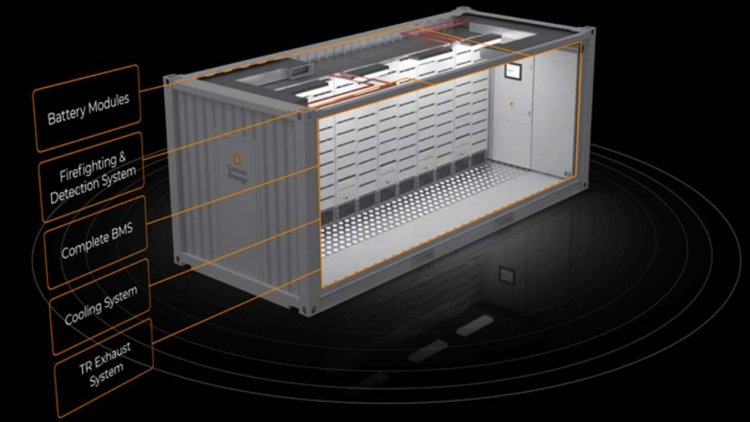
The Corvus BOB is a standardized, class-approved, modular battery room solution available in 10-foot and 20-foot ISO high-cube container sizes.
The complete energy storage system (ESS) comes with battery, battery monitoring system (BMS), cooling, TR exhaust, and firefighting and detection system. The “Plug and Play battery room” simplifies integration into any system integrator’s power management system on board a ship.
Though Corvus started on a container concept back in 2016, Shell has been the major driving force behind the modular and standardized thinking. The energy major believes that owners and operators of many vessel types will benefit significantly from the flexibility offered by a modular, containerized battery system.
Bo Jardine, Shell’s Global Category Manager – Marine, responsible for chartering offshore support vessels (OSVs), says:
“Batteries are going to be on board as the industry decarbonizes, regardless of which fuel are used now or in the future. The benefit of a containerized battery system is that you can add more containers if additional capacity is needed or move containers to another vessel in your fleet if charter contracts or operational requirements require it. It is easy to exchange the ESS when new technology is available and take the ESS off for a second life on shore. Upfront builders’ risk in the shipyard is reduced via the ability to pre-test and assure the battery solution before integration into a vessel. Furthermore, costly rework to the vessel is avoided and turnaround to change battery capacity is faster.”
The Corvus BOB will also provide a supporting gateway for the integration of future fuels technologies such as hydrogen fuel cells into vessels.

Ronald Hansen, SVP Ship Solutions at Corvus Energy and project lead, says:
“The Corvus BOB is a flexible, cost-effective energy storage solution that reduces complexity and risk for the system integrator, shipowners and design companies. With the Corvus BOB, they get a fully approved stand-alone battery room without having to spend time on the configuration inside. The BOB is suitable for both retrofits and newbuilds and we are confident that the solution will enhance project planning and schedules in addition to save time and cost for transportation, installation and commissioning. Being a fully scalable ESS with a standard ISO footprint also makes it an ideal solution for projects where increased capacity is needed. We will continue working closely with all integrators to provide them with the best possible solutions.”
The first Corvus BOB system will incorporate the Corvus Orca ESS, the world’s leading battery system suitable for a wide range of vessels including offshore vessels, cruise and ferries, merchant vessels, workboats and fishing vessels. The system will be DNV-GL type approved.Efraim Kanestrøm, VP Sales at Corvus has worked closely with shipowners and operators in the development phase of the product. He said:
“We are extremely happy to have the Corvus BOB ready for the market as we see a big need for a standardized plug and play solution to simplify battery installations for both shipowners and integrators. The ISO container footprint on the battery room It is a well-known standard and makes the transportation and installation predictable for all parties.”
In the near future, standardized Corvus BOB containers will be available with the full range of Corvus batteries, so that customers can choose the battery type and unit size best suited for each project application. Use of a common BMS will enable combinations of Corvus ESS with different characteristics to be installed and operate in concert to provide optimum energy and power availability.