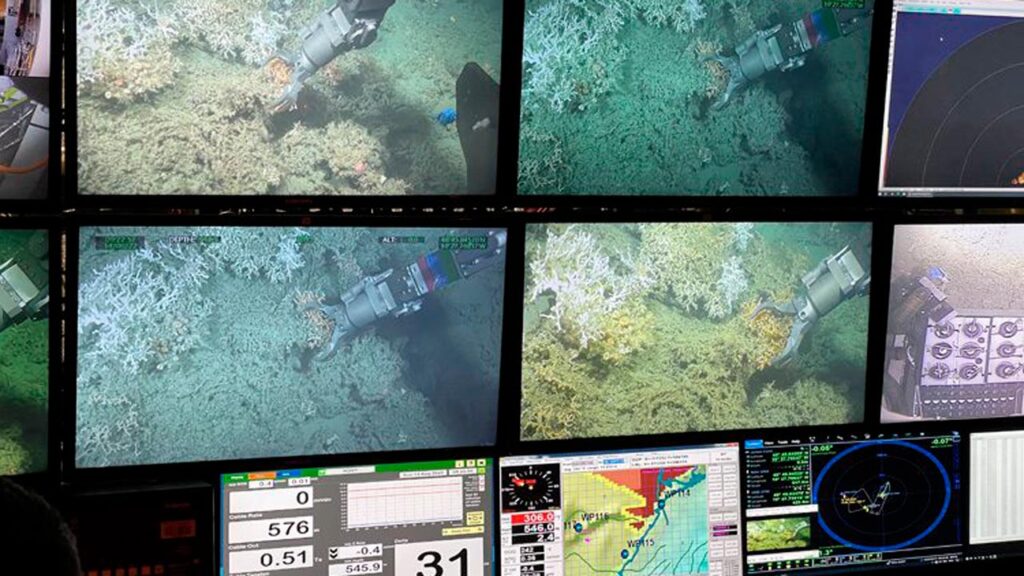
Deep-sea scientists who have recorded ‘unusual’ behaviour from what they believe is a new species of squid say the discovery highlights the lack of understanding in such ocean environments.
Caught on camera by a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) 4,000 metres below the surface of the Pacific Ocean, the squid – nicknamed by the researchers as the ‘muddy squid’ – buried its head in the sediment, leaving its tentacles exposed in an effort to seemingly mimic the stalk of a deep-sea sponge.
This is the first time that a cephalopod, including octopus and squid, has been seen in an upside-down, rigid position. While burying behaviour has been seen in some species of octopus, it has never before been observed in squid and, say the scientists, suggests current estimates of biodiversity in the deep ocean may have been underestimated.
The finding has been published in the journal Ecology.
The report’s lead author Alejandra Mejia-Saenz, a PhD student at the Scottish Association for Marine Science (SAMS) in Oban, said: “This was an example of the weird things you see in the abyss and also highlighted how little we know about that world.
“This is only the second time that a squid has been spotted here in more than 40 years of research. We think this squid could belong to the family Mastigotheuthidae, which includes the whiplash squid, but the behaviour we saw was very strange. Before it got spooked by the ROV, the squid may have been concealing itself from potential predators, or this may be a way of catching prey, which settle on the tenacles that, to us, look like the stalks of a sponge.
“Many people tend to think of abyssal plains as deserts in the deep sea, but there’s probably a higher level of diversity than we think, given the elusive behaviour of these creatures.”

The observation was made in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone of the Pacific, between Mexico and Hawaii, during a research cruise led by the National Oceanography Centre (NOC).
The ROV, known as ROV Isis, was launched from the RRS James Cook and operated by NOC. It was running transects of the seabed as part of the SMARTEX project, a Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) funded investigation into the potential impacts of deep-sea mining in the region.
The ROV had three cameras set at different angles. One was facing forward, parallel to the seabed, another forward-facing camera was angled downwards, and the other one sat underneath the ROV, perpendicular to the seafloor.
Dr Bethany Fleming at NOC was the first to examine ROV footage. She said: “I was scrolling through the videos leading up to the moment where a squid seemed to appear out of nowhere and spotted two long white tentacles emerging from the sediment.
“It was so exciting and unexpected to observe burying behaviour in a deep-sea squid, something that has never been seen before! More discoveries await us in the deep-sea.”