DNV will lead the process safety study to identify the main environmental, safety and operational risks for the world’s first offshore hydrogen production facilities.
Lhyfe, a producer and supplier of green and renewable hydrogen for transport and industry, and Centrale Nantes, is a French School of engineering and research centre, and manages SEM-REV offshore test site.
Lhyfe and Centrale Nantes’ ambitious goal is to make offshore renewable hydrogen a reality, by demonstrating the reliability of an offshore electrolyser. It represents a world-first at a time when initiatives for offshore green hydrogen production are emerging across Europe.
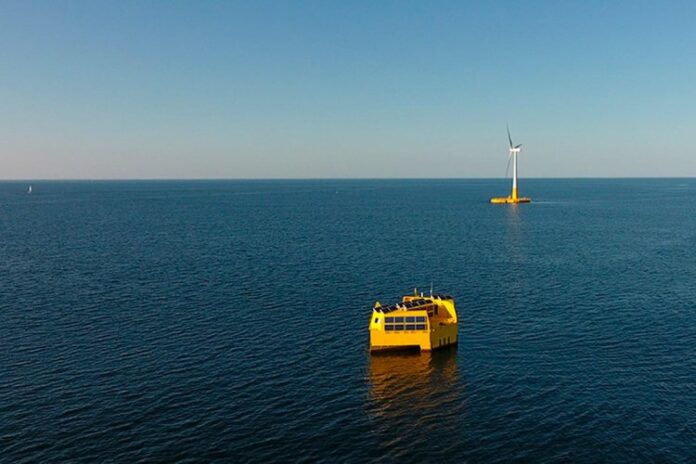
Located off the coast of Le Croisic, France, the green hydrogen-generating system is intended to be powered by electricity from a floating wind turbine, with a target start-up date in 2022.
As part of the design of the new facility, DNV’s experts will undertake workshops and technical sessions to identify and analyse the main environmental, safety and operational risks associated with the project.
Santiago Blanco, Executive Vice-President and Regional Director Southern Europe, MEA and LATAM, Energy Systems at DNV says:
“This is potentially a watershed project, one we are excited to be supporting during the FEED stage. Proving the safety of such activities, particularly with new technologies, to gain acceptance and move them closer to adoption, is vital for the industry and stakeholders.”
“Working with Lhyfe and Centrale Nantes to further their ambitions is something we are pleased to announce, as we believe green hydrogen at-scale is the ultimate destination for the future of energy storage.”
Risks which will be investigated by DNV include the floating barge, fuel cells and hydrogen production. A regulations and standards review will also be included as part of the study.
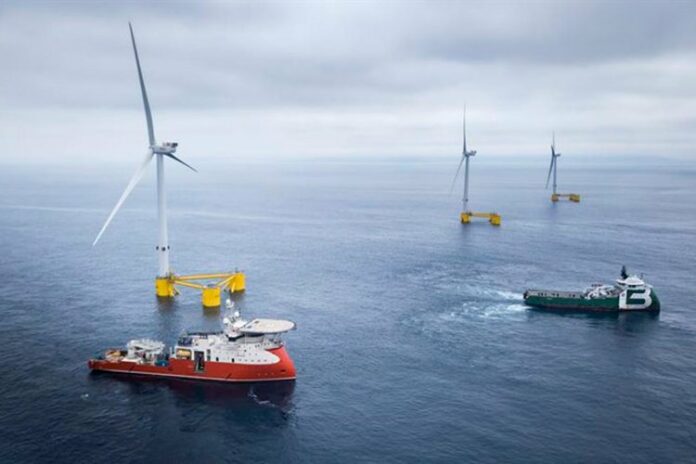
The offshore electrolyser will be installed on GEPS Techno’s floating platform and connected to the various sources of Marine Renewable Energy (MRE) available on the offshore test site, including the Floatgen floating wind turbine. This unique production process only emits oxygen, no CO2 during the operation. Centrale Nantes is also making its research facilities available and providing support for the various regulatory, experimental and logistical phases to ensure a successful outcome.
Hydrogen is a unique energy carrier with no carbon emissions that can be used for long-term storage and heating applications. By using electricity generated from renewable sources such as wind, the resulting energy carrier is carbon-free ‘green’ hydrogen. The economically viable use of green hydrogen becomes feasible due to the increasing penetration of wind and solar power in the years to come.