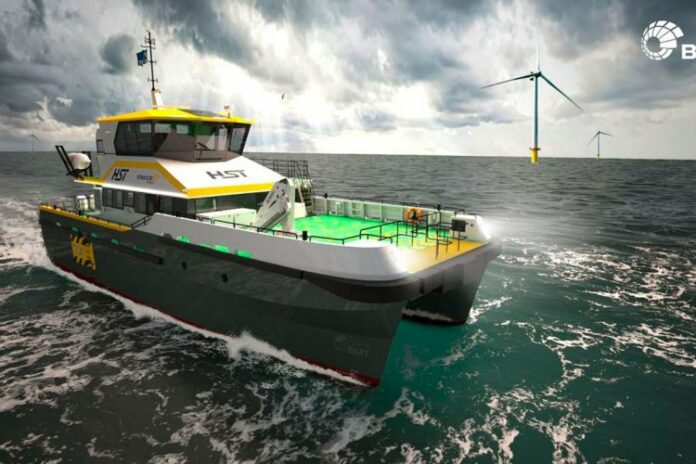
Strategic Marine is forging into the burgeoning green maritime space with an order for four hybrid StratCat 27 (SC27) Crew Transfer Vessels (CTVs) for a new customer, Purus Wind’s HST Marine.
The inaugural order for parallel hybrid SC27s will see the four vessels being delivered in the first and second quarters of 2023. If the options for two additional vessels are exercised, the additional pair will be delivered in third quarter 2023.
Acquired by low-carbon maritime energy transportation and infrastructure systems provider Purus Marine earlier this year and now under its offshore wind business Purus Wind, HST Marine has been expanding its current fleet of vessels rapidly with a quick succession of hybrid CTV orders in particular. Purus Wind provides CTV and commissioning/service operation vessels (C/SOVs) to its customers and will also be expanding its fleet of hybrid C/SOVs.
The BMT-designed StratCat 27 is well-suited to meet the needs of the rapidly developing offshore renewables sector and Strategic Marine’s build-to-stock programme gives it an advantage in meeting tight delivery schedules amid global supply chain challenges.
Mr Tom Nevin, CEO of HST Marine and Business Head of Purus Wind says:
“We are excited to be working with Strategic Marine on this new project and look forward to these new vessels joining our fleet soon.”
The hybrid ready StratCat 27 design was launched in May 2021 and has already seen wide interest from the offshore wind industry, where solid operational capabilities and a reduced environmental footprint are key requirements.
Strategic Marine’s Chief Executive Officer, Mr Chan Eng Yew says:
“We are delighted to have won this order with HST for our first hybrid StratCat 27 which will serve the demanding European offshore wind sector.
“The confidence shown in ordering our new design demonstrates Strategic Marine’s growing reputation for producing reliable, high-quality vessels designed to our customers’ requirements that meet stringent delivery demands.”
The 27-metre vessel was designed for optimal operational efficiency across a wide range of loading conditions, with a hull form that maximizes waterline length and reduces emissions and fuel consumption. A maximum speed of 26 knots enables operators to transport customers quickly and efficiently.
Accommodations and bridge deck layout have been refined with feedback from vessel operators and customers. Post-Covid, real-world adaptations have been made to reduce the risk of infectious disease on operations, meeting Bureau Veritas biosafety notations.
Meanwhile, cabin design has been optimized for improved comfort and workflow, with ample storage space, comfortable sleeping areas and business class seating for 24 offshore service/industrial personnel and three crew members.
The vessel’s bridge deck layout has been enhanced to give improved visibility from the helm and an ergonomic layout to increase comfort for the bridge crew.
In line with the stringent environmental demands of the market, the vessel also features a Green Passport.
Strategic Marine’s recent collaboration with Sea Forrest Power Solutions and Danfoss Power Solutions builds on this increasingly popular design with a retrofittable hybrid power option for vessels delivered without the systems installed at delivery.
The parallel hybrid system enables a reduction in main engine hours and maintenance costs, significant reduction in vessel noise and vibration and, depending on the vessel’s operational profile and charging facilities, can significantly cut the vessel’s operational carbon footprint.
In recognition of this, Strategic Marine has specially designed a unique logo that will denote this and other future hybrid-powered vessels in its range.